43 concave lens ray diagram
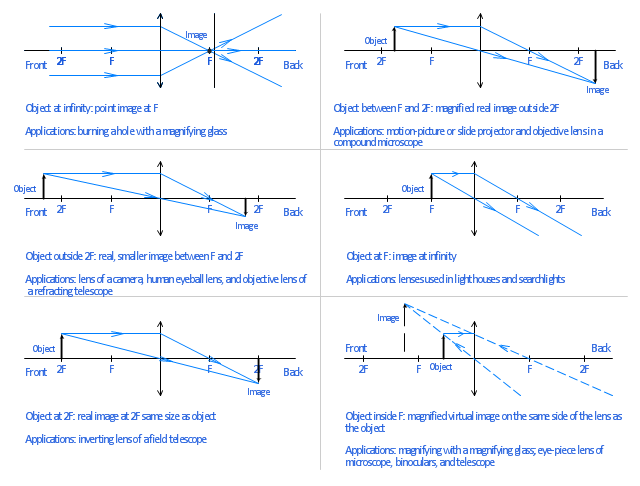
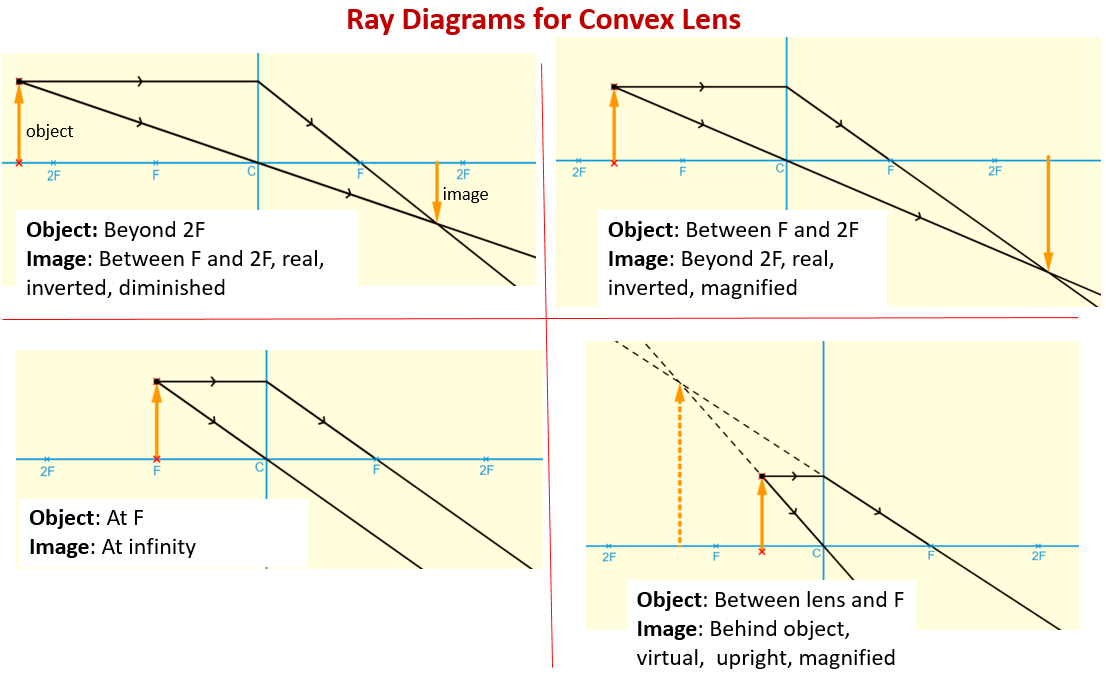
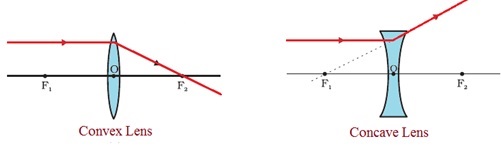
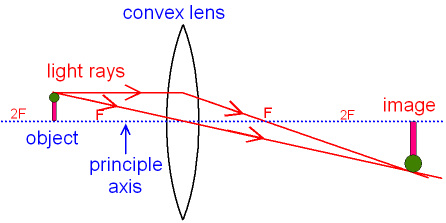
oxscience.com › ray-diagrams-for-lensesImage formation by convex and concave lens ray diagrams Apr 11, 2020 · The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ... byjus.com › physics › concave-convex-lensesConcave and Convex Lenses - Image Formation | Curvature ... When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Ray Diagrams for Concave Convex Lenses - YouTube Using ray diagrams and calculations to find images in convex and concave lenses. Concave Lens Ray Diagrams for Light and Optics Part 5.
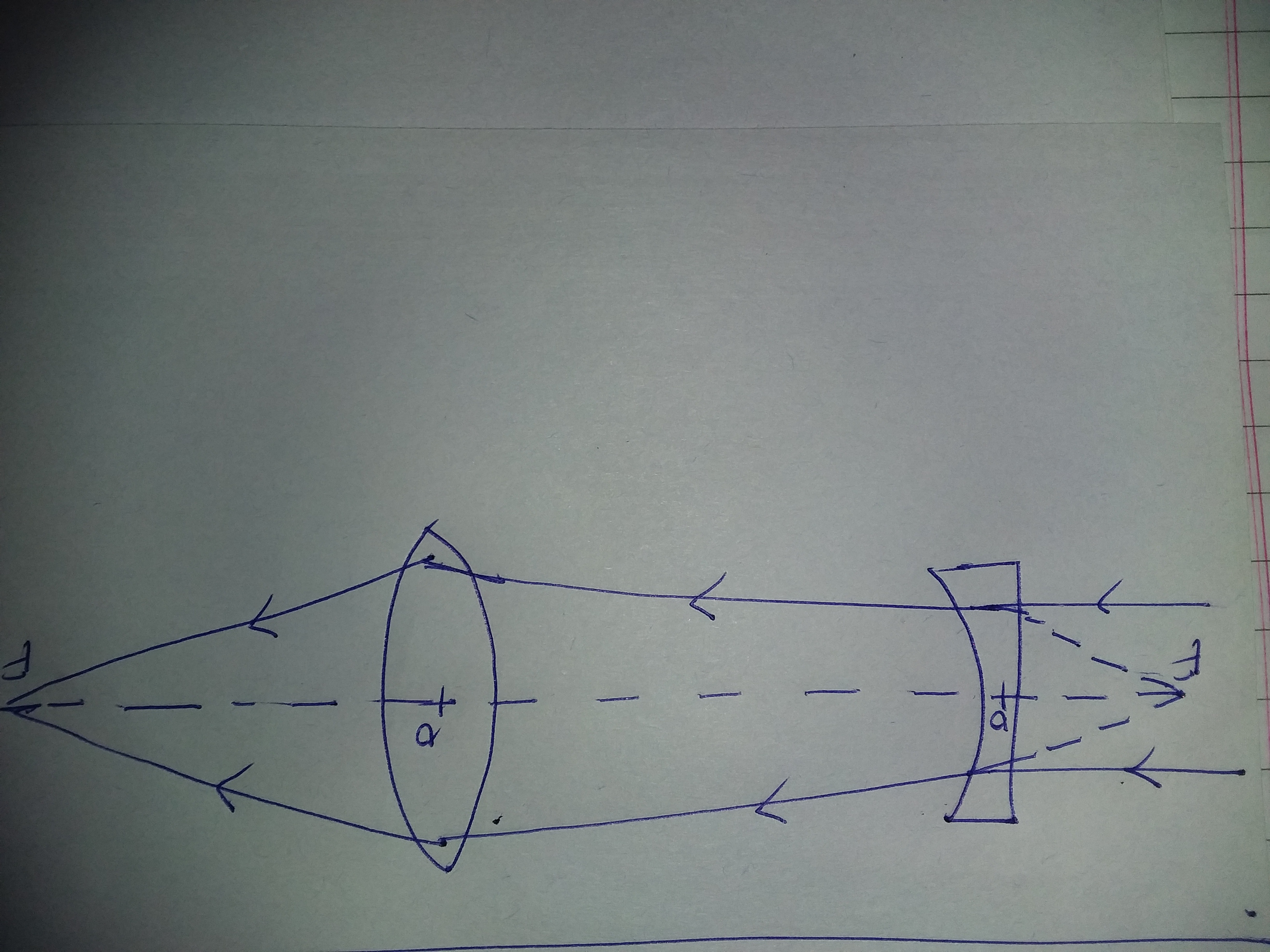
Concave lens ray diagram
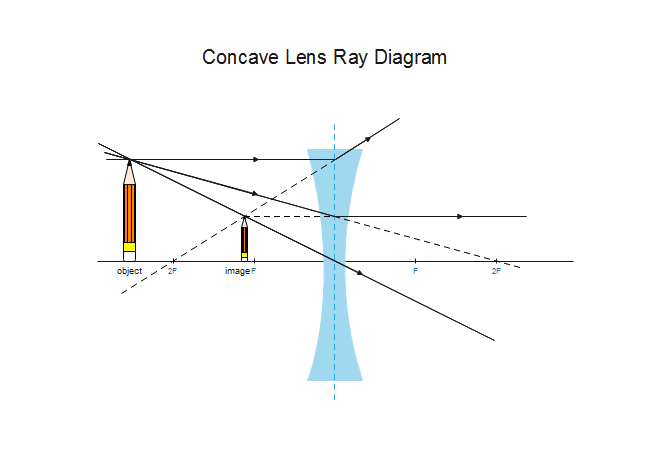
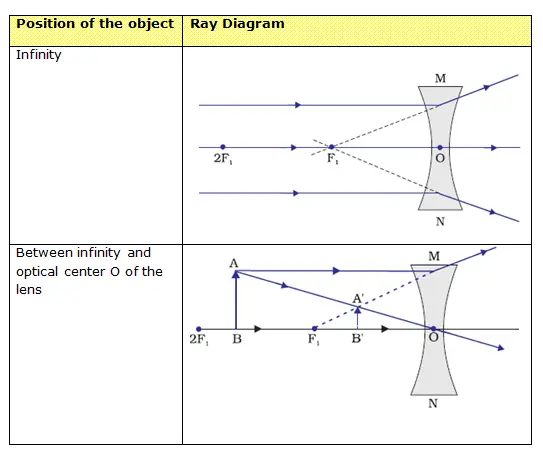
Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps - Teachoo For a Concave lens, There are only 2 cases. They are. Object is Placed at Infinity. Object is Placed between Infinity and Optical Center. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance). So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. › class › reflnPhysics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ... A ray diagram of a concave lens Main Difference - Concave vs. Convex Lens. Lenses are transparent objects with a curved surface. Due to the law of refraction, light rays bend as they enter and Once we draw a ray diagram, we can determine how the lens would form an image. We use several terms to describe properties of an image
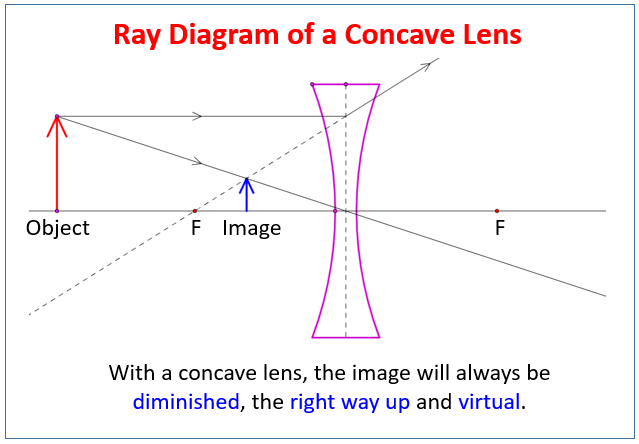
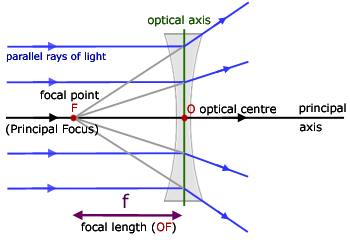
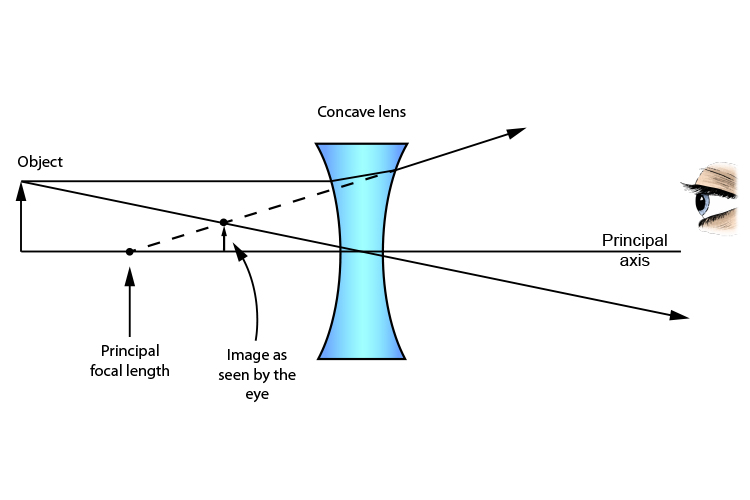
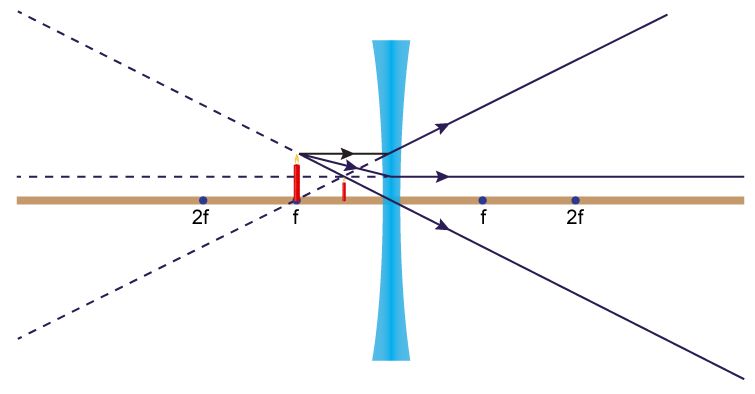
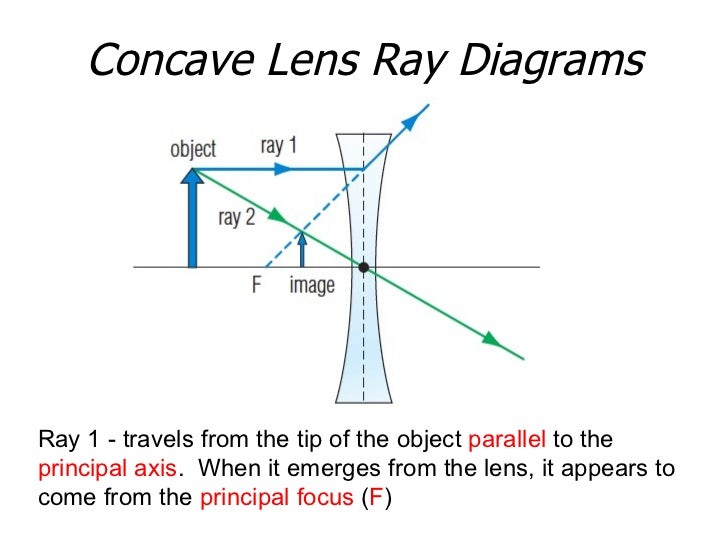
Concave lens ray diagram. Concave Lens Ray Diagram | Free Concave Lens Ray Diagram... Guess you want to draw a professional looking concave lens ray diagram? Try Edraw template which could be applied easily. Just go for more optional ray diagram symbols in the Edraw diagram design library for better drawing. Concave and Convex Mirrors - Ray Diagrams... - GeeksforGeeks Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex mirror, which is when the object at infinity and the object between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. PDF 1. Shine the ray box at a concave lens. Observe how the rays are... Concave Lenses and Ray Diagrams. A concave lens causes light rays to bend away from each other, or diverge (Figure 6.4). To understand why this happens, remember what you learned about refraction in Chapter 5. As light rays travel from a less dense medium, such as air, into a more dense... › 6-waves › 6-3-opticsConvex & Concave Ray Diagrams (6.3.2) | AQA GCSE Physics ... Concave Lens Ray Diagrams. Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case; If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way:
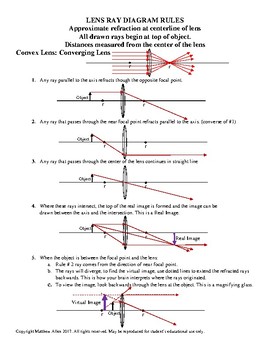
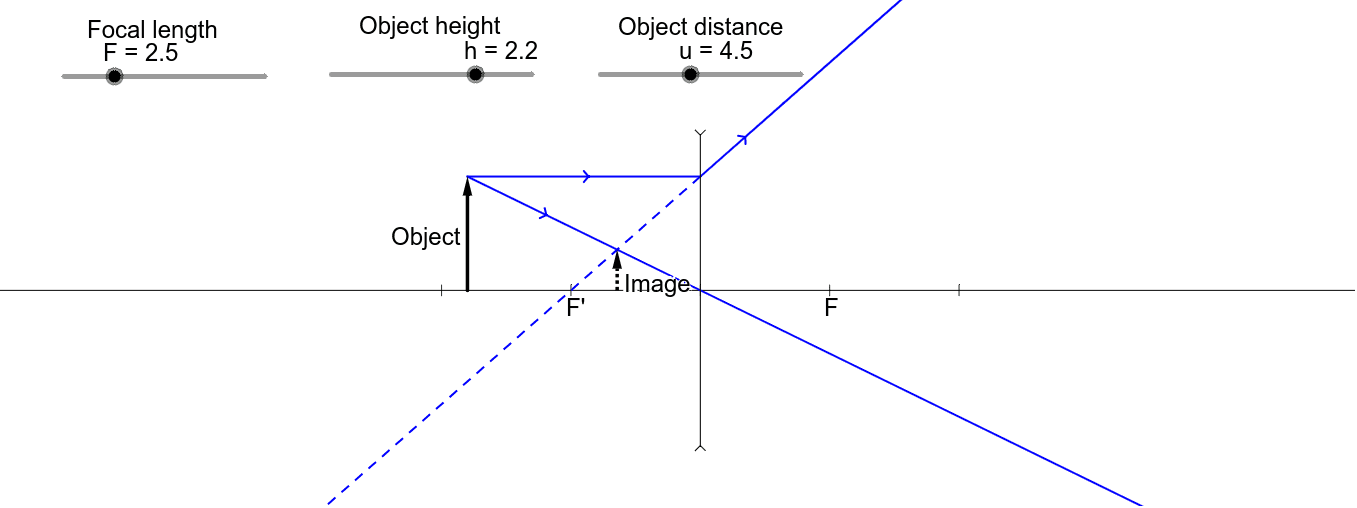
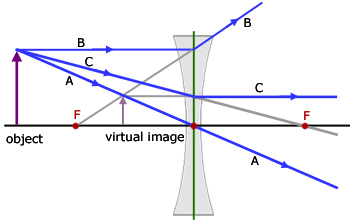
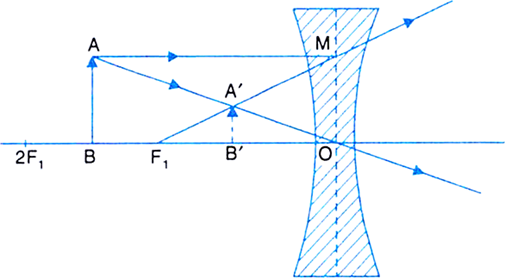
Convex & Concave Ray Diagrams | AQA GCSE Physics Revision Notes Concave Lens Ray Diagrams. Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case. If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way Convex and Concave Lens Ray Diagrams - Juany's Science Blog A lens that causes light rays initially parallel to the central axis to converge is (reasonably) called a concave (converging) lens. We can graphically locate the image of any off-axis point on such an object (such as the tip of the arrow in Fig2 (a) by drawing a ray diagram with any two of three special... Nature of Images by a Convex and Concave Lenses - With Ray... Concave lens form virtual and erect image on the same side of the lens between F1 and O. It is always diminished. > Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of the image by a point object on the principal axis of a spherical convex surface separating two media of refractive indices n1 and n2... Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams Refraction by Lenses. Image Formation Revisited. Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams. The ray diagram above illustrates that when the object is located at a position beyond the 2F point, the image will be located at a position between the 2F point and the focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
Ray tracing diagram for convex lens | Optics - Vector stencils library Wikipedia] The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software The vector stencils library "Optics" contains 17 symbol icons: reflecting surface; convex and concave lens with and without optic axis, body or ray... Ray Diagrams for Lenses - ppt video online download 14 Concave Lens Ray Diagrams All ray diagrams start with a center line and the lens Note: the lens can be simplified into a straight vertical line. 15 Locate and label the focal points: F (real focal point) and F' (virtual focal point) The center (C) is located where the lens intersects the center line Draw the... Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses... Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image. A ray diagram of a concave lens Main Difference - Concave vs. Convex Lens. Lenses are transparent objects with a curved surface. Due to the law of refraction, light rays bend as they enter and Once we draw a ray diagram, we can determine how the lens would form an image. We use several terms to describe properties of an image
› class › reflnPhysics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ...
Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps - Teachoo For a Concave lens, There are only 2 cases. They are. Object is Placed at Infinity. Object is Placed between Infinity and Optical Center. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance). So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis.

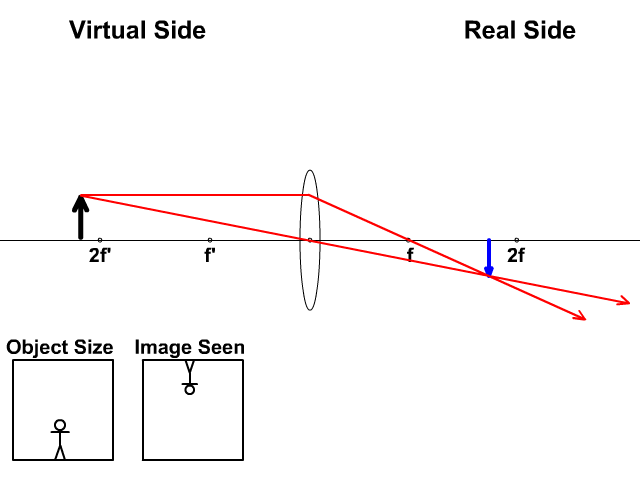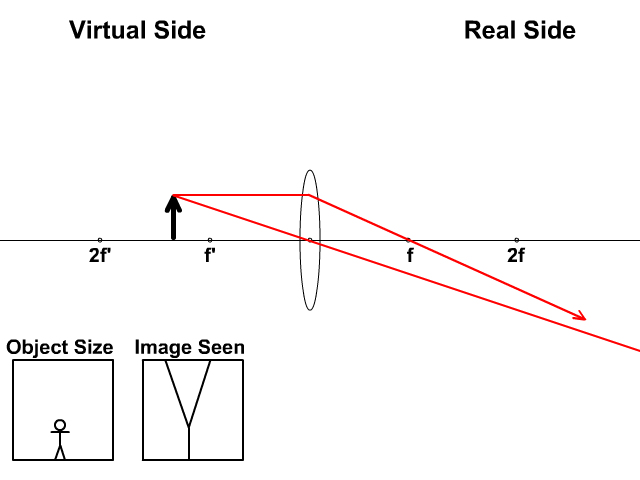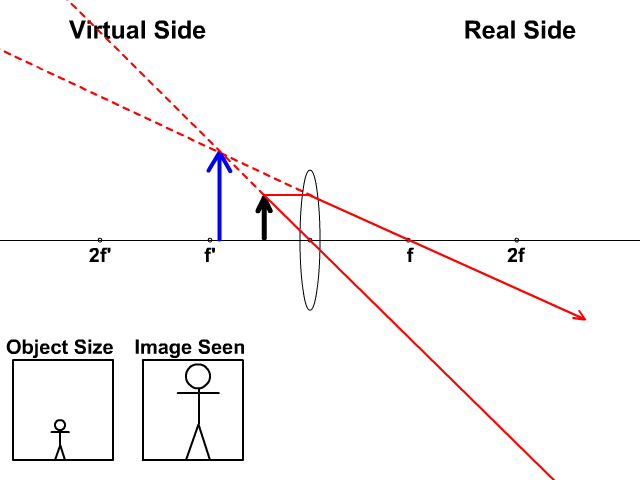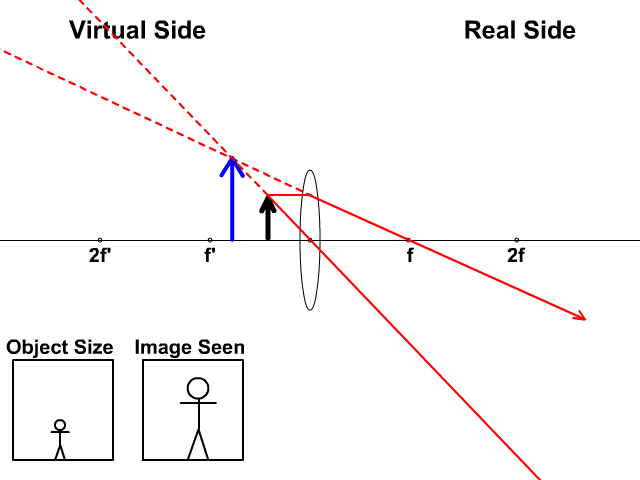
















Comments
Post a Comment