41 pure compound diagram
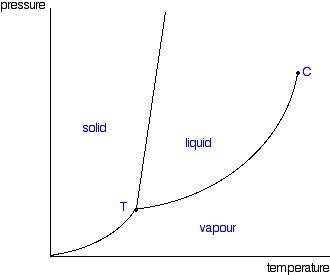
A pure substance does not have to be of a single element or compound. A mixture of two or more phases of a pure substance is still a pure substance as long as the chemical composition of all phases is the same. Phases of a Pure Substance A pure substance may exist in different phases. Transcribed image text: Consider the phase diagram of pure compound. Which statement applies? (A) The path A rightarrow C represents sublimation. (B) Following the C the compound would first liquefy and then vaporize.(c) If the compound is in state A, continued reduction of pressure (at constant temperature) will cause it to melt.
The phase diagram for a compound is shown below. Describe the phases and transitions as the pressure is increased from 0.5 atm to 1.2 atm at a constant temperature of 75 °C. A gas or vapor may be liquefied only at temperatures(A) equal to the normal boiling point.(B) above the normal boiling point.(C) above the critical temperature.(D) at or ...

Pure compound diagram
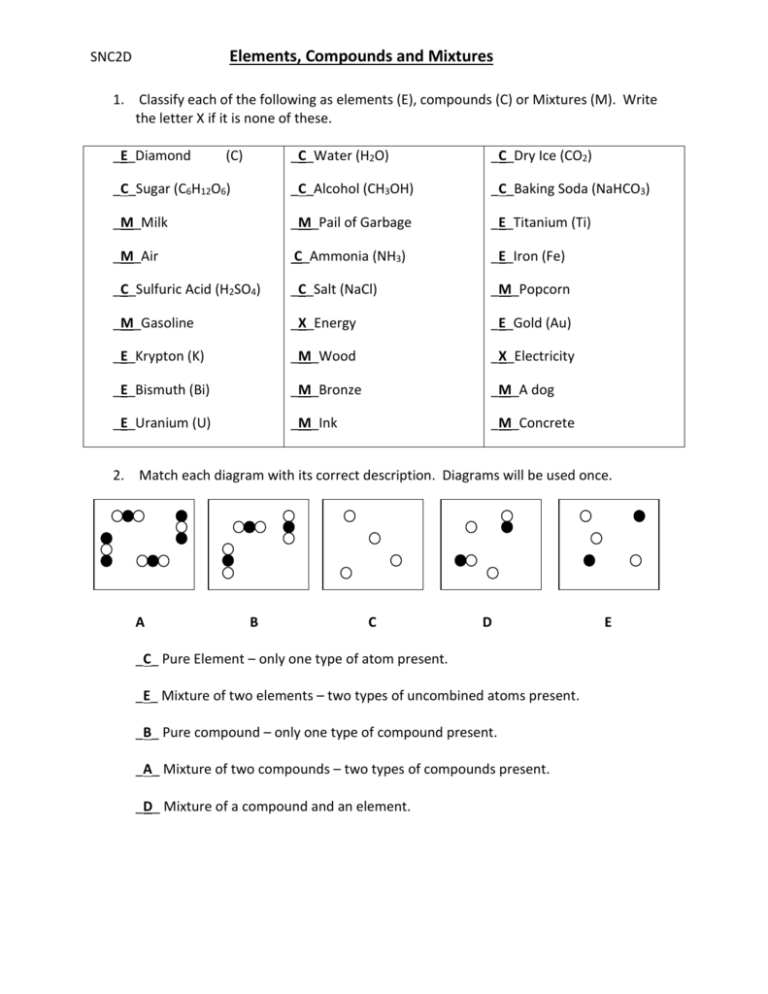
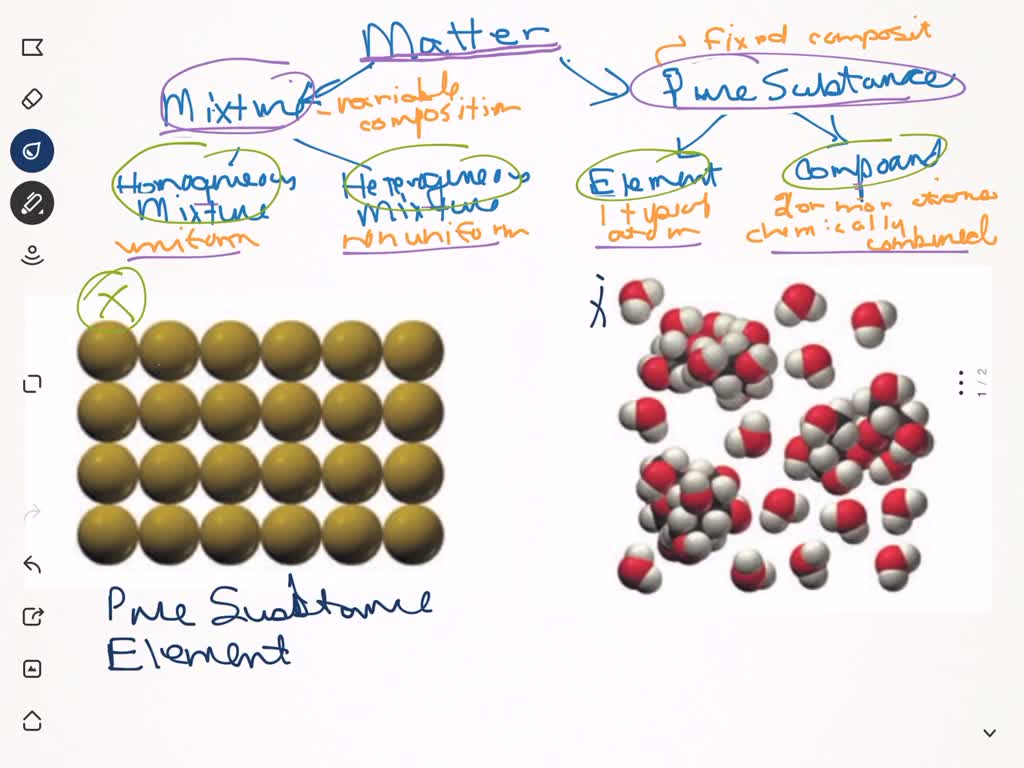
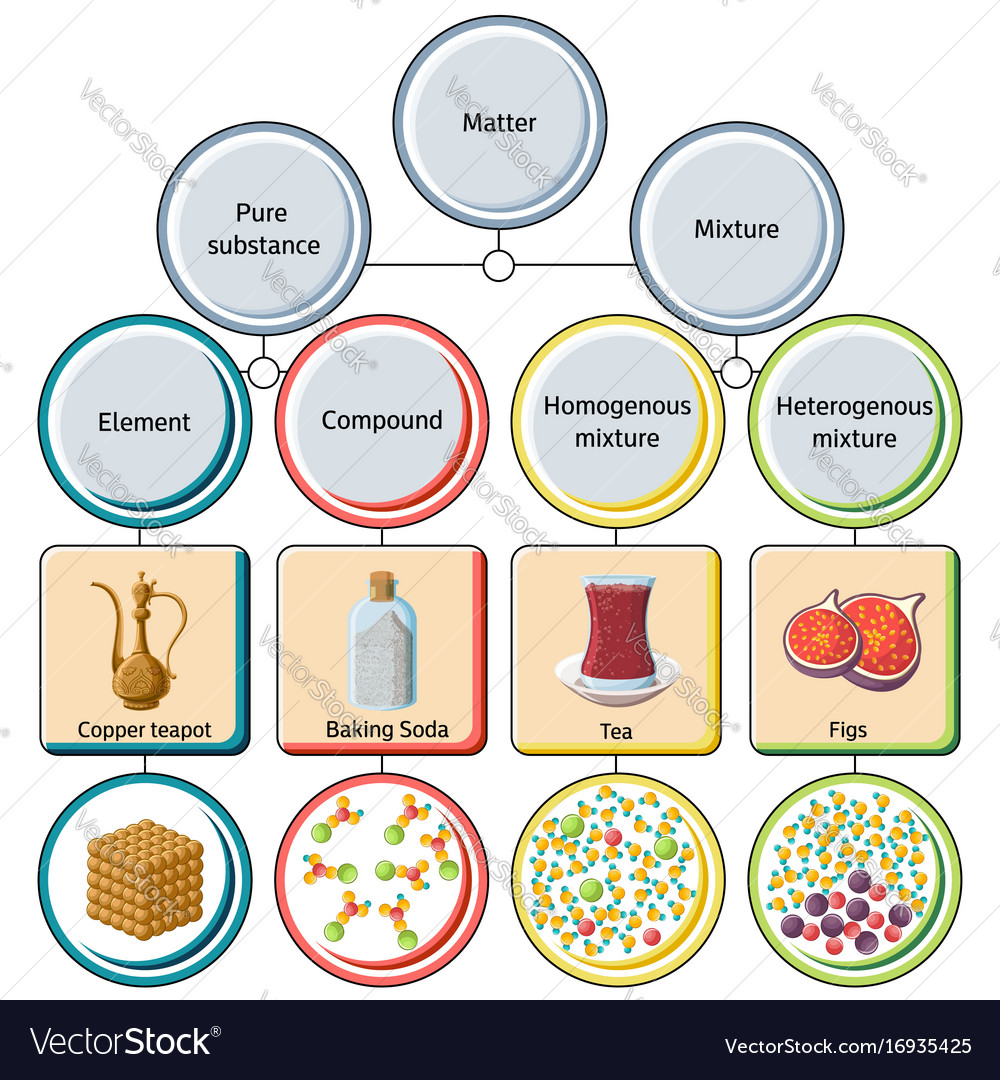
Pure compound – only one type of compound present. _A_4. Mixture of two compounds – two types of compounds present. _D_5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Part 4: Column A lists a substance. In Column B, list whether the substance is an element (E), a compound (C), a Heterogeneous Mixture (HM), or a Solution (S). Diagrams to show the difference between elements, compounds and mixtures. The two diagrams on the left (a and b) summarise what we know about the particles in elements, namely that an element can consist of atoms or molecules, but that the atoms in a certain element are always of only one kind. From the class melting point data, the melting point diagram was constructed (Table 1). The pure compounds in the graph show the smallest melting range and all the mixtures exhibit broader melting ranges and overall melting point depression as compared to the pure solids. The eutectic point appears to lie between 33% and 75% (mole %) naphthalene.
Pure compound diagram. for a pure compound are given in the three diagrams below. In the CinChE manual, you can find a detailed description for the PVT diagram on Page 3-18. Check your textbook for a detailed description of the PT or phase diagram.\r\rWithin a homogenous region or phase \(liquid, vapor, gas, or fluid\), specifying two\ We're being asked to determine which is a pure compound. Recall that Matter can be categorized as a single or variable composition. • Matter is considered a pure substance it is composed of a single entity. Pure substances can be further categorized into two: 88% (50 ratings) Sign up for free to view this solution. Pure Element - only one type of atom present. _E_2. Mixture of two elements - two types of uncombined atoms present. _B_3. Pure compound - only one type of compound present. _A_4. Mixture of two compounds - two types of compounds present. _D_5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Part 4: Column A lists a substance. In Column B, list ... diagrams. •A particle diagram is a box in which coloured balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. •These diagrams can represent elements and compounds, as well as their molecular composition by the types of balls and how they are connected. Element Compound Mixture of an Element and Compound
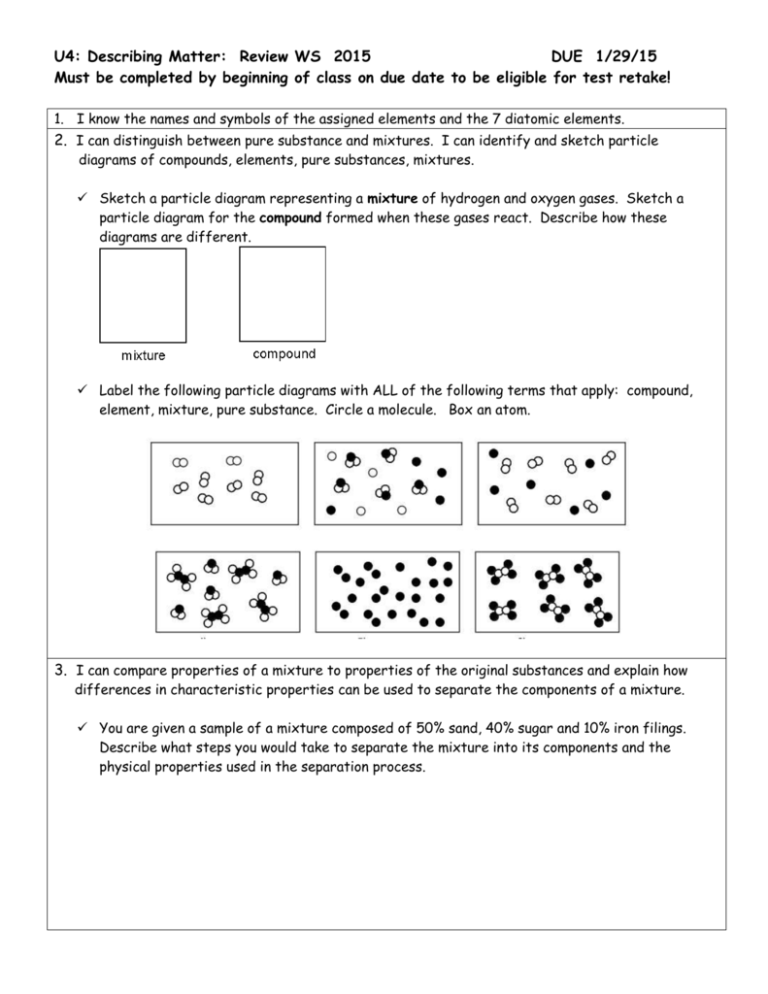
Which particle diagram represents one pure substance, only? C) Given the sirrple representations for oftwo elen-mts: O = an atom of an element = an atom of a different element Which particle diagram represents rmlecules of only one compound in the gaseous phase? Given the diagrarÏË X, Y, and Z below: KEY: Atom of element A = O Pure albite melts (or crystallizes) at 1118 o C, ... solid solution, (f) incongruently melting compound. Draw examples of phase diagrams that show the following - be sure to label everything. a phase diagram that has an intermediate compound that melts incongruently. Answer (1 of 8): Well.. Pure Compound: Pure element or compound contains only one substance, with no other substances mixed in. Impure materials may be mixtures of elements, mixtures of compounds, or mixtures of elements and compounds. 27.Describe diagrams X, Y, and Z using the following terms: Pure substance Monatomic Element Diatomic Element Binary Compound Ternary Compound Mixture of elements Mixture of compounds You may use more than one term for each diagram.
mixture. A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. compound. A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds. pure substance. A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties (one type of particle) element. Types of compounds. Based on elements present; Oxides – When a compound contains one or more oxygen atoms. Generally, metals tend to form oxides fast. (MgO) magnesium oxide or ferrous oxide. (Rust) Hydrides – When a compound contains one or more hydrogen atoms.. Halides – When a compound contains one or more halogen atoms.. Organic – When the compound contains carbon and hydrogen. following questions using the diagrams in the blocks. You must classify the matter in each block A to F using only the numbers 1 - 6 to identify the following categories: Each question may have more than one answer! 1. Element 2. Compound 3. mixture of elements 4. mixture of compounds 5. mixture of elements and compounds 6. a pure substance -5-Experimental determination of a phase diagram Thermal analysis techniques •T = f (t) cooling curves measurements for several compositions)Pure compound: Fusion/Solidification or allotropic transition ↔solidification at 1 transition temperature)Binary solution: Fusion/Solidification ↔solidification in a range of temperature
The diagrams above show the ultraviolet absorption spectra for two compounds. Diagram 1 is the absorption spectrum of pure acetone, a solvent used when preparing solutions for an experiment. Diagram 2 is the absorption spectrum of the solute for which the absorbance needs to be measured to determine its concentration. ... A student has samples ...
Pure compound - carbon dioxide Mixtures A particle diagram for a mixture has more than one type of atom which are not chemically bonded together, or more than one type of molecule. For example,...
Download scientific diagram | The DSC diagram of pure compound 1. from publication: Dielectric and DSC Studies of the Bicomponent Systems with Induced Antiferroelectric Phase Comprising Cyano ...
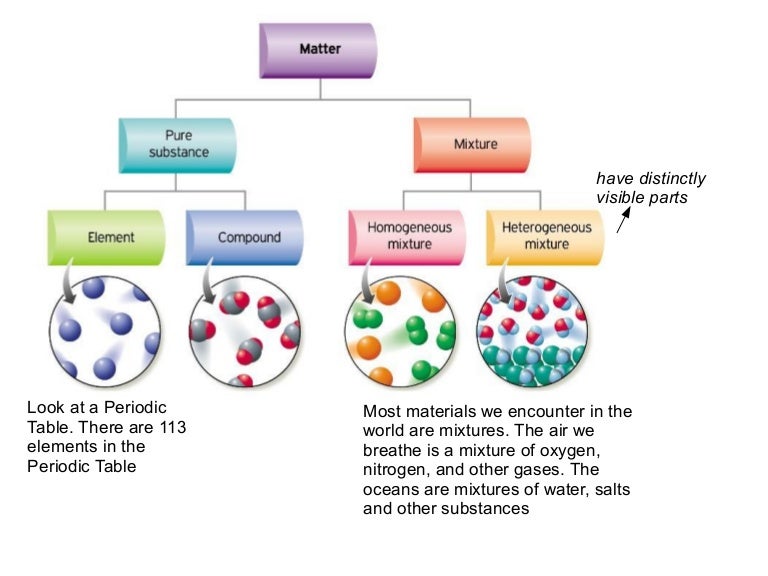
Pure substances and mixtures The meaning of pure. The word 'pure' is used in chemistry in a different way from its everyday meaning. For example, shops sell cartons labelled as 'pure' orange juice.
A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance.
Pure compound – only one type of compound present. _A_4. Mixture of two compounds – two types of compounds present. _D_5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Part 4: Column A lists a substance. In Column B, list whether the substance is an element (E), a compound (C), a Heterogeneous Mixture (HM), or a Solution (S). (Remember a solution is a
Atoms, elements, and compounds are all pure substances. Venn diagrams are used to compare and contrast groups of things. A chemical substance may be either an element or a compound. You can edit this venn diagram using creately diagramming tool and include in your . Source: www.researchgate.net A venn diagram showing elements, compounds, mixtures.
Oct 28, 2019 · Science, 29.10.2020 07:15, Grakname Pure compound diagram
The following diagrams show the molecules in two pure substances before mixing, and the mixture of molecules afterwards. Look at the diagrams closely, and label each of them as either a single substance, or a mixture. 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ Elements, compounds and mixtures (2) – page 4 of 8 C C C C C H H H H H H C C C C C H C H H H H C C ...
Phase Diagrams Revised: 1/27/16 3 The phase diagram in Figure 1 is for a pure compound. When a second compound is introduced to the system forming a homogeneous solution however, the phase diagram drastically changes. For example, the addition of a solute to a pure solvent (making a solution)
A pure compound. A mixture of two compounds. A mixture of a compound & element. Tags: Question 20 ... The diagram can be classified as an element and a molecule. The diagram can be classified as a compound. The diagram can be classified as a mixture of two compounds. The diagram can be classified as a mixture of two elements. Tags: Report Quiz ...
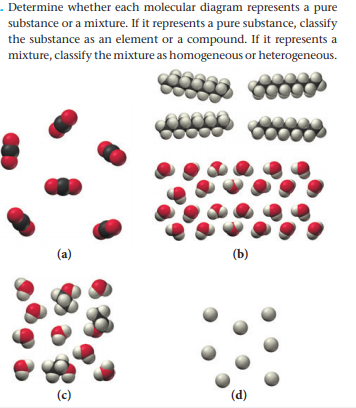
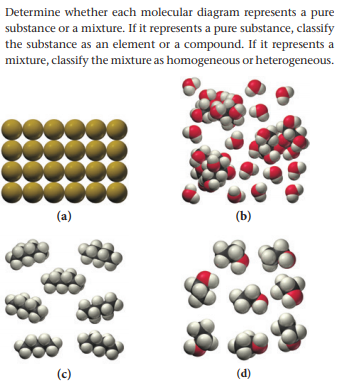
Transcribed Image Text. molecular diagram represents a pure substance or a mixture. If it represents a pure substance, classify the substance as an element or a compound. If it represents a mixture, classify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous. Determine whether.
2- True The most frequent technique to depict the aspects of a compound is with a P-T diagram. For distilled water, draw a P-T diagram. Any pure substance can be represented by a P-T diagram. The dissolution line is the boundary between the solids an… View the full answer
Particle Diagrams Elements: one type of atom (single or diatomic) Compounds: 2 or more types of atoms bonded together Mixtures: combination of elements and/or compounds ... Pure Compound Pure Element Mixture of Compounds Mixture of Elements Mixture of Compound(s) and Element(s) IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAM IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAM ...
From the class melting point data, the melting point diagram was constructed (Table 1). The pure compounds in the graph show the smallest melting range and all the mixtures exhibit broader melting ranges and overall melting point depression as compared to the pure solids. The eutectic point appears to lie between 33% and 75% (mole %) naphthalene.
Diagrams to show the difference between elements, compounds and mixtures. The two diagrams on the left (a and b) summarise what we know about the particles in elements, namely that an element can consist of atoms or molecules, but that the atoms in a certain element are always of only one kind.
Pure compound – only one type of compound present. _A_4. Mixture of two compounds – two types of compounds present. _D_5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Part 4: Column A lists a substance. In Column B, list whether the substance is an element (E), a compound (C), a Heterogeneous Mixture (HM), or a Solution (S).























Comments
Post a Comment